A Comprehensive Overview: Different Types of Printers, Their Advantages, And Disadvantages
Introduction
Printers are an untangling puzzle for many. With various types available, each offering distinct features, advantages, and drawbacks, it can be challenging to determine which type serves your needs best. This article provides an exhaustive overview, a profound comparison, and user-friendly answers to related questions. Discover the confidentiality of printers, their types, and how they differ in functionality, advantages, drawbacks, and fitting different needs.
What Exactly is a Printer?
A printer is essentially an external hardware output device that takes data stored on a computer or other digital systems and generates a hard copy of it. For example, it permits us to print photos, documents, spreadsheets, and other files from our computers into a physical format.
Here are some key aspects:
- Data Conversion: A printer's primary function is to translate the digital information into a format that can be understood and displayed on paper.
- Connection Type: Most often, printers are connected to a computer via a cable or WiFi for seamless data transmission.
- Size & Type: Printers range from small, portable, personal ones to large, industrial machines designed for large-volume output.
- Utility: They are ubiquitous across various sectors, such as homes, schools, workplaces, healthcare facilities, and much more.
- Function: These devices immensely simplify our workflow by producing tangible copies of electronic documents.
What Are the Different Types of Printers?
There's a broad array of printer types available in the market, each tailored to different needs with its specific technology. Let's delve into some of the most popular ones:
1. Inkjet Printers: These versatile printers operate by spraying fine droplets of ink onto the paper. They are best-known for their ability to print vibrant colors splendidly, making them ideal for photo printing.
2. Laser Printers: Stepping into commercial territory, laser printers function using an electrostatic digital printing process that efficiently delivers high-quality text and graphics. Excelling in speed and volume, they're perfect for office spaces that need large amounts of fast, sharp printing.
3. Thermal Printers: With silent operation, these printers utilize heat to produce images on thermochromic paper. Businesses requiring receipts and barcodes often prefer thermal printers due to their inkless operation.
4. Dot Matrix Printers: Ideal for continuous printing like invoices or receipts, these antiquated yet effective devices work by striking an ink-soaked cloth against the paper using a print head.
By understanding the technologies rimming the realm of printers, one can make an informed decision suited to specific requirements.
Advantages of Different Printer Types: Which Printer Should I Choose?
In the quest to choose the ideal printer for your requirements, acquainting yourself with the various types and their benefits can be instrumental. Here is a rundown of the common printer types and their corresponding advantages:
1. Inkjet Printers
- *High-Quality Prints*: Capable of producing superior-quality images with detailed color reproduction.
- *Affordability*: Compared to other types, they are reasonably priced, making them suitable for individual or small office use.
2. Laser Printers
- *Efficiency*: Ideal for high-volume printing, laser printers are faster, delivering more prints within a shorter period.
- *Cost-Effectiveness*: Though they may carry a higher initial cost, their per-page expense could be lower in the long run due to their high yield.

3. Thermal Printers
- *Silent Operation*: These printers are silent, making them suitable for use in quiet environments such as libraries.
- *No Ink Needed*: Unique in their operation, thermal printers do not require ink but specialized paper that responds to heat.
4. Dot Matrix Printers
- *Lower Operating Costs*: With minimal requirements, these printers are economically efficient for businesses.
- *Continuous Printing*: Due to their unique printing mechanisms, dot matrix printers are ideal for businesses needing constant print outputs like receipts and barcodes.
It’s vital to bear in mind that while these advantages form a general guideline, individual models within these categories may vary significantly. Therefore, before zeroing in on your printer choice, it's advisable to consider:
- *Print Volume*: High-volume requirements are best catered to by laser printers.
- *Quality Needs*: For vibrant color prints, turn to inkjet printers; for crisp textual prints, laser printers are ideal.
- *Cost Constraints*: Inkjets printers tend to be cheaper initially, though laser printers could be more cost-effective over time.
- *Operational Aspects*: Each printer type has operational distinctions in terms of speed, noise levels, ease of use, and other factors. Choose based on your convenience and specific needs.
So, understanding what each printer type offers can help you make a fitting choice aligning with your printing needs.
Disadvantages of Different Printer Types: What Are the Downsides I Should Expect?
Grasping the weaknesses of the different types of printers helps in making a precise purchase decision. Identifying the potential pitfalls of each printer type also improves understanding of when and where their usage is optimal.
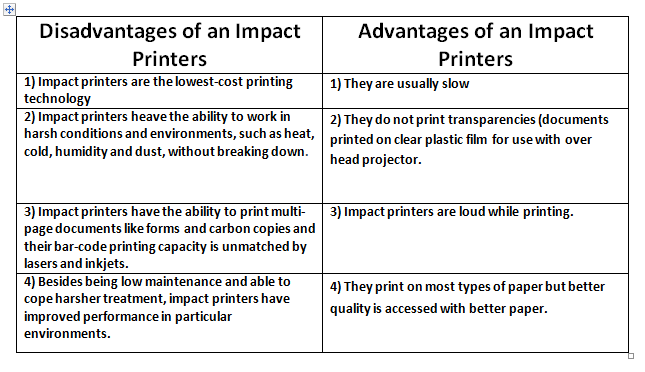
1. Inkjet Printers:
- *Speed:* A marked disadvantage of inkjet printers compared to others is their slower speed, particularly when printing a high volume of papers.
- *Running Costs:* When you print a lot, the higher cost per page compared to laser printers can quickly add up and be more expensive in the long run.
2. Laser Printers:
- *Initial Expense:* Although cheaper to run in the long term, laser printers often come with a significant upfront cost.
- *Photograph Printing:* While laser printers excel in text and graphic printing, they often fall behind inkjet printers when it comes to printing high-quality photographs.
3. Thermal Printers:
- *Maintenance Expense:* The requirement for special thermochromic paper can add to the overall operating cost of thermal printers.
- *Print Lifespan:* The print quality from thermal printers may fade over time, especially when exposed to heat or sunlight, impacting long-term record keeping.
4. Dot Matrix Printers:
- *Noise:* Dot-matrix printers are generally the noisiest of all types. Navigating this problem requires a quiet work environment or sound isolation.
- *Quality:* The print quality of dot matrix printers often leaves much to be desired compared to their counterparts. They're better suited for straightforward text and data output, like receipts and invoices.
Ultimately, the choice of printer should resonate with your particular needs and environment. While each printer type has its drawbacks, they all have specific scenarios where they can potentially outshine the others.
How Can I Determine the Best Type of Printer for My Needs?
Pinpointing the ideal printer for your unique needs doesn't have to be an enigma. By considering the following crucial factors curated carefully considering your potential printing needs, you can effectively decide the type of printer that embeds seamlessly into your workflow:
1. Assess the Volume of Printing Requirements:
Your volume of printing plays a pivotal role in dictating the ideal printer type for you. A laser printer is an economical choice for executing high-volume print tasks more efficiently. These massive yet cost-efficient machines can handle a vast quantity of print jobs, promising a lower cost per page.
2. Examine the Level of Quality Required:
If your workflow demands vibrant color prints with high-quality visuals, an inkjet printer will astound you with its performance. Also, for a crisp, sharp print with far superior text quality, a laser printer is an unbeatable choice.
3. Consider Your Budget:
It's imperative to comprehend how different printers align with your budget expectations. While inkjet printers are less costly initially, their cost per page can add up significantly over time. Conversely, laser printers may have a higher upfront cost but offer a lesser per-page cost in the long run, thereby providing more cost-effectiveness for high-volume needs.
4. Reflect Over Speed, Noise, and User-friendliness:
Key considerations such as the operation speed, noise levels, and the overall ease of use also significantly impact your printer selection. For instance, though Dot Matrix printers can be loud, they serve certain business scenarios efficiently with a low-operating cost factor. On the other hand, thermal printers operate silently but demand a special thermal paper, resulting in extra expenses.
Rest assured, addressing these four pivotal considerations can transform this complex decision-making process into a pleasantly simple experience. Indeed, the correct printer type will perfectly match your requirements, promoting streamlined workflow and enhanced productivity.
Conclusion
In closing, printers come in multiple types, each serving specific use-cases with their benefits and drawbacks. From household use to large businesses, knowing what to expect from each type can guide you in making an informed decision that meets your needs.
Related FAQs about what are the different types of printers advantages and disadvantages
Are there significant benefits in choosing an inkjet printer over a laser printer?
Yes, inkjet printers are excellent for color prints and can deliver high-quality photos, making them ideal for creative pursuits. They are also generally less expensive initially, making them a feasible choice for personal use or small offices.
What are common issues I might encounter with thermal printers?
Some common issues with thermal printers include the need for specialised thermal paper, which can elevate operating costs. Moreover, prints from these printers may fade over time when exposed to heat or sunlight, affecting long-term recordkeeping.
How does a dot matrix printer serve different needs from other types of printers?
Dot matrix printers are particularly beneficial for tasks requiring constant print output, such as invoices or receipts. They have low operating costs and are robust, making them ideal for environments where sturdy hardware is needed like industrial settings.