Understanding 3D Printers: Comprehensive Overview of the Pros And Cons
Introduction
3D printers, with their astonishing capabilities, have revolutionized various aspects of technology and industry. While these intriguing contraptions hold great potential, there are still several pros and cons that users should carefully consider before getting on board with this technology. This article offers a comprehensive overview of these aspects, providing valuable insight to help you make an informed decision about using 3D printers.
What Exactly is 3D Printing?
3D printing, more formally referred to as additive manufacturing, is a transformative technology that turns digital designs into three-dimensional physical objects. This process involves:
- Starting with a Virtual Design: The initial step involves creating a digital design of the object you aim to print. This blueprint serves as the guiding light for the 3D printer itself.
- Layer-by-Layer Addition: The printer then sequentially adds layer after layer of material, be it plastic, metal, or otherwise, to ultimately shape the desired object. Each of these layers can be seen as a thinly sliced horizontal cross-section of the object.
- Crafting Complex Structures: One of the most striking features of 3D printing is its ability to craft incredibly intricate designs and structures otherwise unattainable by traditional manufacturing methods.
Armed with a 3D printer’s capabilities, boundaries are pushed, and the realm of what is possible widens immensely.
How Does a 3D Printer Work?
A 3D printer operates through an intricate but comprehensible process. These are the pivotal steps that it embraces to output a three-dimensional object:
1. Slicing the 3D model: The initial stage involves partitioning a 3D model into numerous horizontal layers, each layer representing a cross-section of the resulting object.
2. Sending the blueprint to the Printer: Once the digital representation is ready, the sliced layers are transferred to the 3D printer.
3. Layer-by-Layer Construction: The 3D printer then proceeds by depositing material layer after layer, meticulously crafting the predefined shape. This process could take a few hours to even days, based on the size and detail level of the model.
Hence, a 3D printer functions systematically, and the transformation of a virtual model into a tangible object materializes gradually, setting the cornerstone of numerous creative possibilities.
What Are the Remarkable Advantages of 3D Printers?
The inherent capabilities of 3D printers offer many impressive benefits that span across multiple sectors. They can bring in significant value for users by introducing unique opportunities for improved customization, cost-efficiency, and greener practices.
1. Enhanced Customization and Creativity:
3D printers are indeed a gateway to limitless creativity and customization. Whether it's about creating intricate architectural models, developing product prototypes, or crafting bespoke jewelry, the technology provides a platform to turn even the most complex designs into reality. Here's an insight into the customization capabilities of 3D printers:

- *Design Flexibility*: You can devise and modify designs effortlessly to cater to specific needs.
- *Prototyping*: Rapid prototyping becomes possible, accelerating the product development cycle.
- *Personalized Products*: Users can create bespoke items catered to individual preferences.
2. Promoting Cost-Efficiency:
Unlike traditional manufacturing procedures that involve expensive molds and assembly lines, 3D printers can create an object in a single step. This process of additive manufacturing minimizes waste, reducing overall costs. Here's how 3D printers promote cost-efficiency:
- *Reduced Production Costs*: Lower initial costs by eliminating the need for molds and assembly lines.
- *Inventory Management*: The on-demand nature of 3D printing minimizes inventory and associated storage costs.
- *Reduced Waste*: 3D printers only use the exact amount of material needed, reducing wastage.
3. Adopting Eco-friendly Manufacturing:
3D printing takes manufacturing into a greener future. It’s an eco-friendly technology that uses resources efficiently, reduces waste, and, over time, can contribute to reduced emissions. Here are some ways in which 3D printers contribute to a greener environment:
- *Waste Reduction*: 3D printers use only the necessary material, avoiding excess waste.
- *Resource Efficiency*: The printers use less energy than traditional manufacturing methods.
- *Lightweight Components*: 3D printed parts are often lighter, leading to fuel-efficiency in vehicles and aircraft.
In essence, the adoption of 3D printers can bring in revolutionary changes, allowing individuals and businesses to enjoy a unique blend of customization, cost-efficiency, and sustainable practices.
What Are the Potentially Detrimental Disadvantages of 3D Printers?
While the advent of 3D printers certainly brings a slew of advantages, it's equally important to evaluate potential downsides that could come with this technology. Understanding these drawbacks will allow for balanced decision-making. Here are the primary concerns associated with 3D printers:
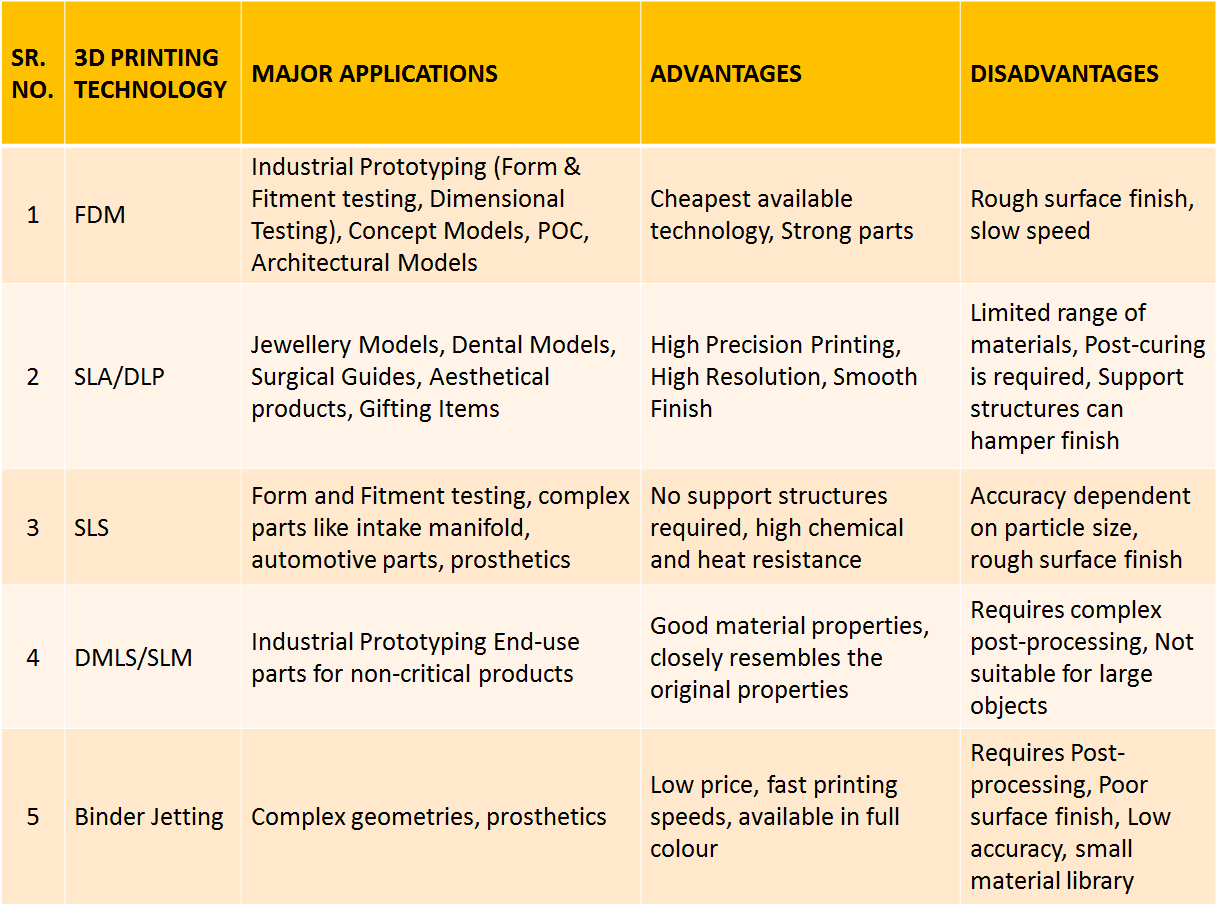
1. Design and Material Limitations: Despite offering substantial creative freedom, 3D printers do face certain constraints.
- Design: Certain structures, such as hollow spaces or overly complex designs, may pose a challenge for 3D printing.
- Materials: The material options for 3D printing are currently not as diverse as those offered by conventional manufacturing techniques. Plastic and metal dominate the industry, limiting job materials choices.
2. Technical Challenges: One needs technological expertise to operate these machines smoothly. Issues could range from:
- Machine Errors: Instances of machine malfunction can lead to operation disruption and time delays.
- Software Glitches: Software problems could potentially lead to design inaccuracies and printing failures.
- Final Product Imperfections: Factors like incorrect settings or sub-par filament quality can result in poor quality output.
3. Legal and Ethical Issues: 3D printing's ability to create any product from a blueprint could lead to several ethical and legal concerns such as:
- Copyright Infringement: The ease of replicating items can lead to unauthorized copying of copyrighted products.
- Counterfeit Goods: The ability to create precise replicas may contribute to the production of counterfeit goods.
- Weapon Production: 3D-printers' potential use for weapon manufacturing raises definite safety and legal concerns.
While these drawbacks don't diminish the revolutionary nature of 3D printing, having a full understanding of such challenges is crucial. This information can help prepare better and make the most out of this game-changing technology.
An Overall Assessment: Is 3D Printing Worth the Investment?
If you're considering adding 3D printing to your business's tech arsenal, you'll want to assess whether such an investment offers suitable returns. There are several variables to consider, including your specific business needs, the scale of your intended projects, and of course, your budget. Here's a breakdown:
The Incredible Upsides
* Personalization and Innovation: With 3D printing, the boundaries of creativity are virtually limitless, empowering you to bring imagined designs to life efficiently. This technology is uniquely poised to deliver tailored solutions that traditional manufacturing methods just can't match.
* Cost Efficiency: 3D printers can significantly reduce production costs over time, despite the initial high outlay. The primary cost benefits come from reduced waste, thus increasing material efficiency, and the ability to 'print on demand', thus decreasing inventory storage costs.
* Environmental Impacts: Besides the impressive economic advantages, 3D printing presents an eco-friendly edge. It not only minimizes waste but also, in certain sectors, facilitates the production of lighter components, leading to more fuel-efficient vehicles which could result in reduced CO2 emissions.
The Potential Downsides
* Design and Material Limitations: Despite the high level of customization possible, there are still some limits. Structures with hollow spaces or complex designs may present challenges. Additionally, the range of usable materials does not yet match that of conventional manufacturing, which could stymie certain projects.
* Technical Issues: As with any technology, users might encounter various glitches, errors, or sometimes an outright failure of the final product caused by incorrect machine settings, subpar filament quality, or flawed design files.
* Legal and Ethical Challenges: The ability to replicate anything might lead users into murky legal waters. The risk of reproducing patented products, counterfeiting goods, or even creating weapons raises serious ethical and legal concerns that society and lawmakers will need to address.
3D printing is an advanced technology that requires a significant initial investment. High-quality 3D printers can have a steep price tag, but, when considering the incredible advantages it can bring, many businesses find the long-term benefits outweigh these initial costs. It’s vital you weigh these pros and cons against your specific needs and ambitions. 3D printing could well be an investment that propels your operation into a new age of efficiency and creativity.
Conclusion
In conclusion, 3D printing is a powerful technology that offers great potential across various sectors. Despite some limitations, its benefits of customization, cost-effectiveness, and eco-friendliness make it a worthy consideration. Like every significant investment, understanding its advantages and drawbacks will enable a more informed decision-making process.
Related FAQs about what are the advantages and disadvantages of 3d printers
How do the benefits of 3D printing outweigh the disadvantages?
The benefits of 3D printing, including cost reduction, waste minimization, and enhanced customization, often surpass its downsides. Despite limitations in design, materials, and potential technical glitches, the freedom to materialize intricate designs and bring raw concepts into reality offers far-reaching advantages in various sectors.
What industries can benefit the most from 3D printing?
Industries like healthcare, aerospace, and automotive can reap significant benefits from 3D printing. It allows for cost-effective production of complex parts in healthcare, lightweight, fuel-efficient components in aerospace and automotive, and rapid prototyping across all these sectors.
What strategies can be used to overcome the challenges of 3D printing?
Overcoming 3D printing challenges involves continuous learning, embracing innovative solutions, and active collaboration between industry and legislative bodies. Regular design optimization, software updates, training, engaging in research and development, and proposing regulatory frameworks can help tackle key challenges in 3D printing.